Iron deficiency anemia affects millions of people worldwide due to low iron levels in the body. When the body lacks enough iron, it fails to produce an adequate number of red blood cells.
These cells are vital for transporting oxygen to every part of the body. Without sufficient oxygen, organs and tissues cannot function properly, leading to a variety of health problems.
Iron is also essential for producing hemoglobin, a protein that helps red blood cells carry oxygen efficiently.
If iron deficiency anemia is left untreated, it can result in serious medical complications, including heart disease and depression. Symptoms vary depending on severity, age, and overall health. Some people experience no noticeable symptoms, while others develop multiple and severe signs.
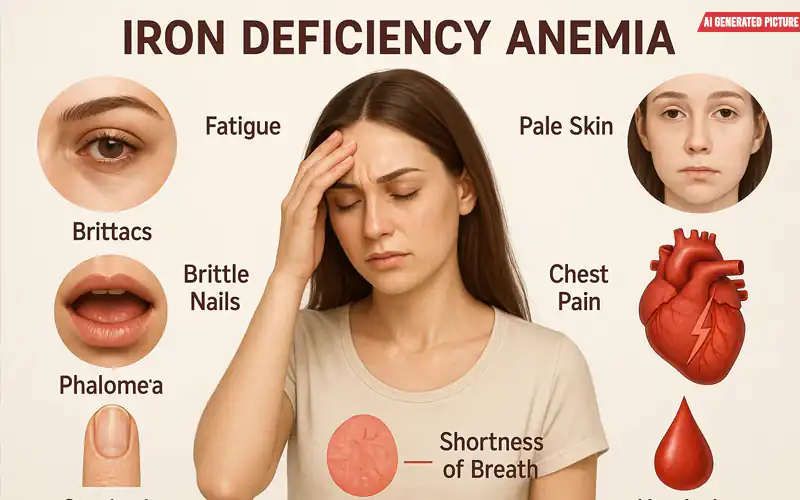
Common signs of iron deficiency anemia
1. Extreme fatigue and weakness
One of the most common symptoms is persistent tiredness. This happens when your body cannot deliver enough oxygen to the cells, reducing energy production. As a result, you may feel slow, weak, and unable to concentrate, even after adequate rest.
While fatigue can stem from many causes, persistent and unexplained tiredness should prompt a medical check-up.
2. Shortness of breath
Healthy people continuously supply oxygen to their heart, muscles, and organs. However, with anemia, oxygen delivery drops, forcing the lungs to work harder. This leads to breathing difficulties, even during mild activities or rest. In some cases, chest tightness may also occur.
3. Rapid heartbeat (Palpitations)
A fast heartbeat may result from stress, medications, or exercise, but in iron deficiency anemia it signals the body’s attempt to compensate for low oxygen. The heart pumps faster to circulate the reduced hemoglobin more quickly. Continuous rapid heart rate can be harmful to cardiovascular health.
4. Pale or yellowish skin
When red blood cell counts drop significantly, less blood reaches the skin, making it appear pale, yellow, or grayish. The body prioritizes blood supply to vital organs, neglecting the skin.
Read More: Reasons behind surge in heart attacks among Pakistani youngsters
5. Headaches and dizziness
Reduced oxygen supply to the brain can cause swelling in blood vessels or increased pressure, resulting in headaches. These may be accompanied by dizziness or a light-headed feeling. Iron deficiency anemia also increases the risk of migraines, which can include nausea and vision changes.
6. Cold hands and feet
Poor blood circulation, caused by low red blood cell counts, often leaves the hands and feet feeling cold. Since the body directs blood toward vital organs, extremities receive less warmth and oxygen.
Less Common but Important Symptoms
7. Ringing in the ears (Tinnitus)
Some patients experience ringing or buzzing sounds. This happens because the heart works harder to maintain blood flow, sending more blood toward the middle ear.
8. Dry skin and hair
Low hemoglobin affects cells responsible for skin repair and hair growth. Inadequate oxygen further dries and weakens skin and hair.
9. Swelling of the tongue and mouth issues
Doctors can sometimes identify anemia simply by examining the mouth. The tongue may appear swollen and pale, with cracks forming around the lips. Some people experience mouth sores or a burning sensation.
10. Craving non-food items (Pica)
An unusual craving for substances like ice, dirt, or wood is a recognized but poorly understood symptom of iron deficiency anemia.
Untreated iron deficiency anemia not only worsens over time but also increases the risk of complications like heart strain, developmental delays in children, and lowered immunity.
Diagnosis usually involves blood tests, and treatment may include dietary changes, iron supplements, or addressing underlying conditions causing the deficiency.
Note: This article is based on medical journal findings. Always consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice.